On the other hand, the stock exchange is a very unstable object with fines and lows, significantly affecting the mood of investors and the economy. The recent period that many investors are worried about was a sharp decline.Prominent worldwide stock market indices, such as the Dow Jones Industrial Average, fell, causing a phenomenal all-over global financial market. As I have highlighted in this article, the most recent stock market crash, why such a massive beating was dealt to the Dow Jones, and what this portends for the economy and investors in the future.
Let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
What happened to the Dow Jones?

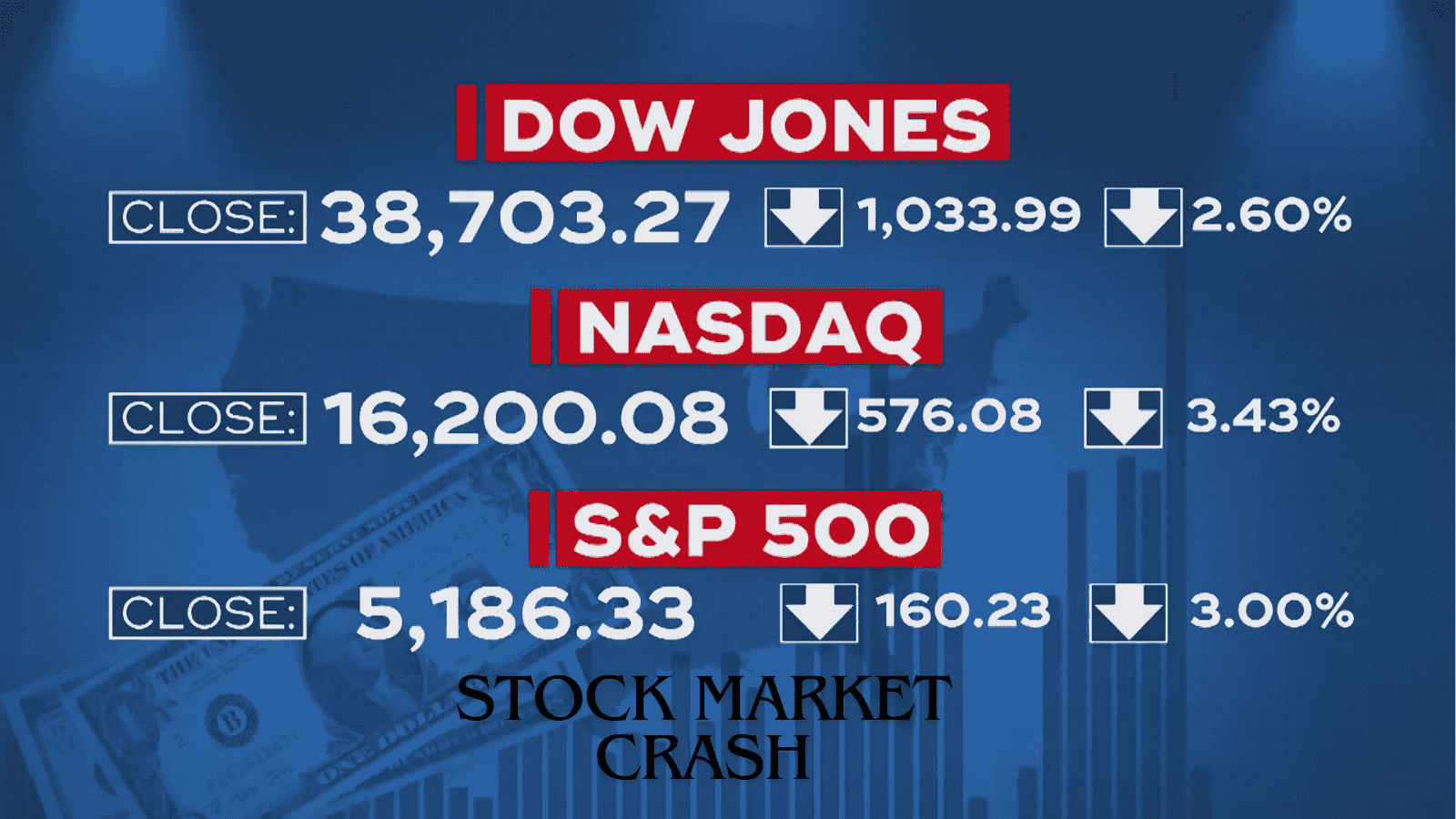
For example, in [insert specific date], the Dow Industrial 30, a representative of 30 large public limited companies in the United States of America, fell by over 1000 points in a single trading session.The loss put the percentage more than 3% down—a significant shift for a major stock market index.
To give context, Dow Jones loses far more of its value and triggers such losses to signify more than a blip on the radar. It’s a shift in the market that tends to be driven by a number of contemplated economic, geopolitical, and financial parameters. It is crucial to disentangle the factors for such a steep decline: learn the world’s economic relations and the actions of investors relying on them.
Effect of the Announcement on Investor Perception
One of the primary impacts of the Dow Jones sharply going down lower was the knock-on effect on investor confidence. Selling, made worse by the same ” year-end cash crunch,” was also pushed by the fear that other share prices would continue to plummet. Small investors, namely the new issue ones, started existing in a bid to reduce their losses in the trading process. This reactionary behavior led to high fluctuations, and large institutional investors were also unwilling to make staged operations.
The drop in the Dow Jones translated to other indices, such as the S&P 500 and NASDAQ, all of which have nosedived.
CAUSES OF STOCK MARKET CRASH

Several precursors, both domestic and international, led to the crash.
Uncertainty about Inflation and interest rates
It was a worry that characterized turmoils in the stock market, and one of them was the inflation issue. Inflation in the last few months was high, and the Federal Reserve responded by aggressively increasing the interest rates. The concept of increasing the rates of inter-bell is to slow the economic activity rate by increasing the cost of funds so that demand will also follow.
However, when the Federal Reserve proceeds to increase interest rates, investors will always fear the effects on the earnings of corporations. Lower credit affordability will mean less spending on credit products, such as cars and houses, which are major credit categories. Thus, many investors began withdrawing their funds from the stock market with expectations that the economy, at best, would slow or, at worst, drop into a recession phase owing to high interest rates.
Geopolitical tensions and Global instability
A further contributor to the loss of such great amounts in the Dow Jones was continuing geopolitical risk factors in different regions. An example is global volatility: the military conflict in Ukraine, the continuing tensions in the Middle East, and the trade relations between the US and China all pressure investors’ confidence. Globally integrated supply chains, which weakened due to the COVID-19 outbreak, received new losses, thus slowing down the economy.
Generally, geopolitical risk implies a threat to investors since it results in a high cost of energy, interrupted supplies, and general instability of the market. The stock market generally takes a knock during such times because of increased operational costs and lower earnings certainty for firms.
Tech Sector Struggles
Apart from financial institutions, high-tech stocks, which are one component of the US stock market, were also to blame for the Dow Jones falling greatly. This was particularly so as most of the leading tech-based firms saw their stock markets decline drastically owing to the dropping of Value relevance measures due to the reorganization of growth prospects. Those companies that benefited from the pandemic era of growth in technology service demands found challenges as consumers became more tempered in their spending and the rates of competition heightened.
For example, Apple, Amazon, and Microsoft are common stocks whose values have declined for years. Regarding inflation and interest rates, tech shares were most affected; they heavily relied on constant expansion and investment.
Corporate Earnings Warnings
When the earnings season was on, many big companies released warning statements that their profits would be below expectations for one reason or another. High cost, low demand, and supply chain disruption all hit numerous companies’ operational gains.
The consequences we observe when a company like [Insert major company name] posts bad earnings are in the figure below. They reveal that investors cannot bear such a shift in the economy’s health. This can lead to a wide sell-off because investors begin to fear that the losses could be symptomatic of a larger issue.
Overreaction of the Investors and Market Sentiments
It has been described in many cases that investments, especially stocks, often experience crunchy moments that are more psychological than real. When the Dow Jones is down, everyone gets irritated and wants to sell, thereby causing a drag. This spawns a vicious cycle of decline, leading to increased sales, which in turn leads to more decline.
The efficiency of media is also a reason for investors’ overreaction, while media emphasizes negative events during stock market fluctuations. Seeing negativity, fear, and uncertainty would mean more people would be let go, further exacerbating the losses.
Stock Market Recovery What to Expect
Despite the current fluctuating situation, many investors seem confused; the fact is clear that the share market can rebound at any point. Markets can rebound after a crash or a correction, but the timelines for this to happen differ. This means investors should invest long-term and not make trades or sell during high volatility. The general idea would be to concentrate on making high-quality investments, which should yield good results irrespective of volatility.
Here are a few potential paths for recovery:
Federal Reserve Intervention
Providing the market deterioration intensifies, or the economic environment deteriorates further, the Federal Reserve could extend other forms of monetary accommodation. So, if rates are lowered, it should be after the signs of the recession. However, a policy change can also help restore the markets and help investors return.
Corporate Earnings Rebound
When the economy returns to strength and becomes stable, most firms may be able to post improved and restored operating profits, which will reflect in their stock prices. If inflation is effectively managed and consumer expenditures improve, corporate earnings may restart their climb in the stock market.
Market Confidence and Market Feel
When panic begins to reduce, and investors regain faith in the market and the ability to recover, the stock prices may stabilize. Generally, they are succeeded by a phase of stabilization, during which many people start searching for beaten-up securities.
Conclusion
The recent heavy downturn witnessed in the Dow Jones resulted from uncertainties arising from inflation and increase, eased interest costs, political instability, and challenges in the technology industry.
Such causes contributed to so much fluctuation, and it is pertinent to note that such market swings are normal in the economic cycle. Despite the vagueness of the short-term outlook in the market, long-term-oriented investors should stick to their objectives and employ rationality while investing.
To those still feeling the barbs of the recent rout, comfort can be drawn from the fact that the market has, in the past, come to life after a crash.
As such, investors can easily understand the volatility by looking at quality investments and planning themselves for future income. The Dow Jones
had a terrible September, which means the market is in a transition phase and will soon be joined by stability and growth.
Is Dow Jones going to bounce back from these big losses anytime soon?
FAQs
- What does it imply for the Dow Jones to lose lots of ground?
It indicates that the stocks of the 30 large companies in the Dow Jones index have decreased significantly, and their value has been downturned. This could be due to several economic factors, including inflation, interest rate adjustments, or any instabilities in the global market.
- What happens when the stock market crashes?
It may directly affect the masses through stock investments, retirement funds, and merchants and indirectly via weakened consumers’ confidence. Should the market increase its downward spiral, more retirement accounts may be valued less, and people will be reluctant to spend or invest even more.
- What should investors do, particularly when the markets are sliding?
The worst thing an investor should do is panic and start panicking when the market is bearish. Invest for the future, stick to your asset mix, and do not sell in a moment of high stress.